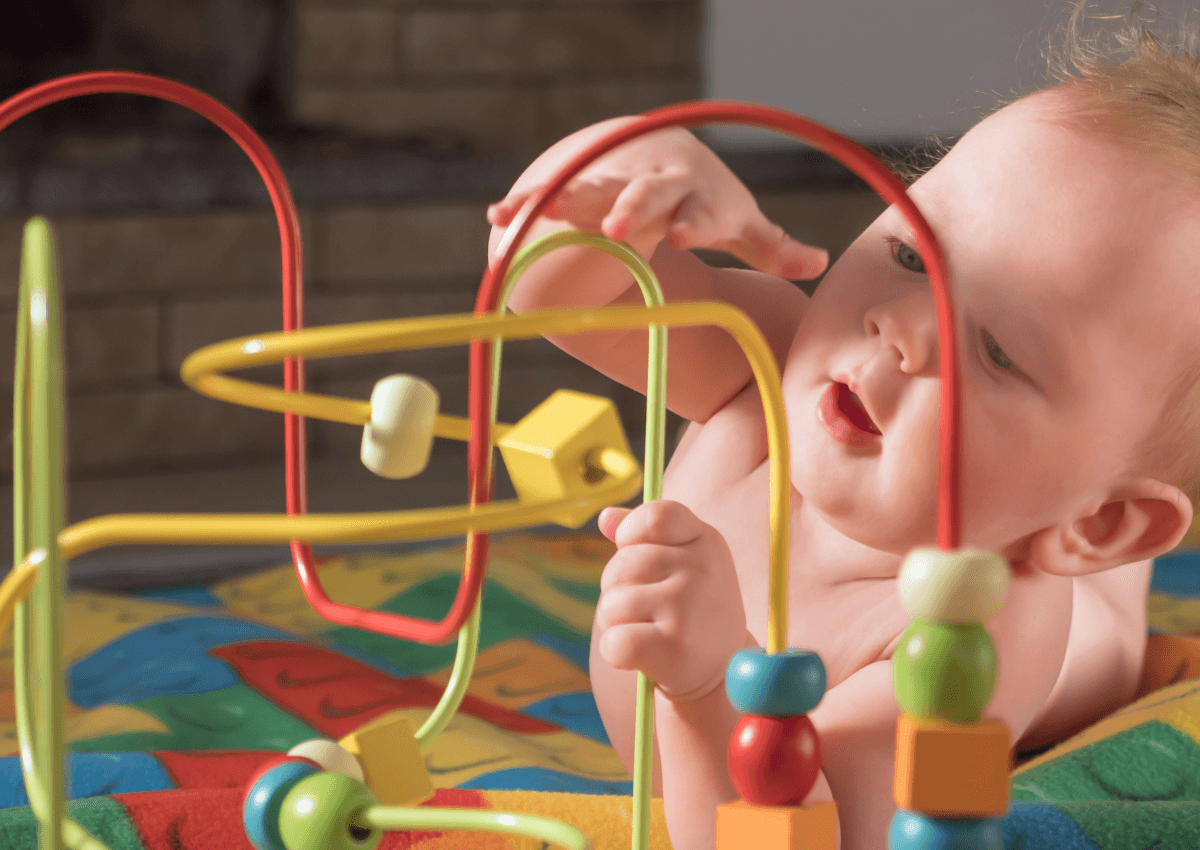
In today’s blog post, I’d like to discuss the benefits of Occupational Therapy (OT) for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD). I believe it’s crucial to create awareness and help families understand how OT can make a positive impact on the lives of their children.
- Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD) Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD) is a condition where the brain struggles to process and organize sensory information from the environment. While these disorders are distinct, they often overlap; children with ASD may also have sensory processing difficulties.
- The Role of Occupational Therapy in ASD and SPD Occupational Therapists are trained to help individuals develop, recover, and maintain the skills required for daily living and working. In the context of ASD and SPD, OT aims to enhance the child’s ability to participate in daily routines, social interactions, and learning experiences. This is achieved through a combination of strategies, including sensory integration therapy, social skills training, and functional skills development.
- Sensory Integration Therapy Sensory integration therapy is a cornerstone of OT for children with ASD and SPD. The goal is to help the child’s nervous system process and integrate sensory information more effectively. OTs use various sensory-rich activities tailored to the child’s needs, helping them learn to tolerate and respond appropriately to sensory stimuli. This can lead to improved self-regulation, emotional stability, and focus.
- Social Skills Training Children with ASD often struggle with social interactions and understanding social cues. Occupational Therapists work with these children to develop their social skills through role-playing, social stories, and video modeling. By practicing these skills, children with ASD can learn to recognize facial expressions, maintain eye contact, and engage in age-appropriate conversations.
- Developing Functional Skills Functional skills are essential for a child’s independence and participation in daily activities. For children with ASD or SPD, these skills may include self-care tasks (e.g., dressing, toileting), fine motor skills (e.g., writing, using utensils), and gross motor skills (e.g., balance, coordination). Occupational Therapists employ various techniques to help children master these skills and improve their overall functioning.
- Collaborative Approach and Family Involvement Successful OT involves collaboration between the therapist, the child, and the family. Family involvement is crucial for generalizing the skills learned in therapy sessions to the child’s everyday life. Occupational Therapists often provide parents with resources, strategies, and support to ensure that the child’s progress continues outside the therapy setting.
Conclusion: Occupational Therapy can play a significant role in improving the quality of life for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Sensory Processing Disorder. Through sensory integration therapy, social skills training, and functional skills development, children can gain the necessary skills to participate in daily routines and social interactions more effectively. Remember, collaboration and family involvement are key to achieving lasting progress. If you believe your child might benefit from Occupational Therapy, contact us for an evaluation and tailored intervention plan.