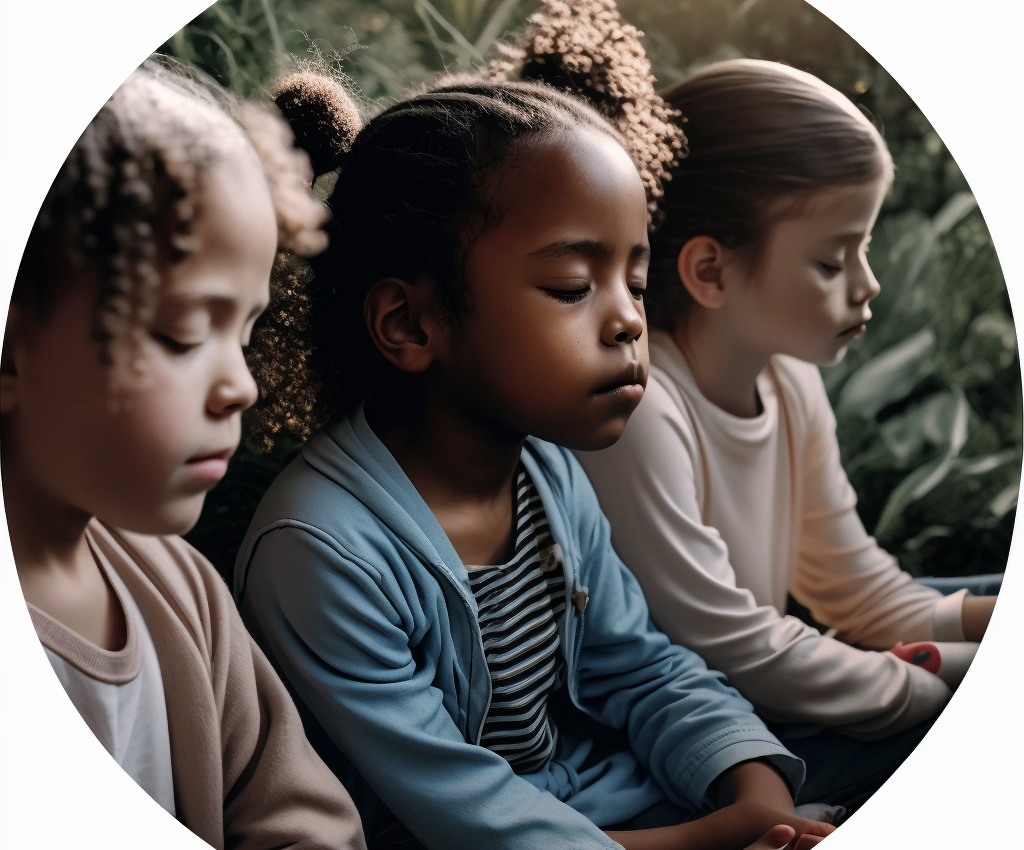
At Dynamics Success Center, a top occupational therapy center in Singapore, we often encounter children and parents grappling with sensory integration challenges. One of the less-discussed aspects of sensory integration is Interoception, which plays a crucial role in a child’s overall well-being and development. In this blog post, we will dive into the world of interoception, its connection to sensory integration, and practical strategies to help children develop this essential skill.
Understanding Interoception
Interoception refers to the perception of our body’s internal state, such as hunger, thirst, pain, temperature, and even emotions. It is the eighth sensory system, working alongside the other seven senses (touch, taste, smell, sight, hearing, vestibular, and proprioception) to create a comprehensive sensory integration framework.
Interoception and Sensory Integration
Sensory integration is the process by which our brain interprets and organizes information received from our senses, allowing us to respond appropriately to our environment. Interoception is a critical component of this process, as it provides essential information about our physical and emotional states. For example, recognizing hunger allows us to seek food, while understanding emotions helps us navigate social situations.
Children with sensory integration difficulties may experience challenges in processing interoceptive information, leading to struggles in self-regulation, emotional management, and social interactions. By focusing on interoceptive awareness, we can help children better understand their internal states and develop coping strategies to manage their sensory needs.
Interoception Strategies for Children
- Body Awareness Activities
To foster interoceptive awareness, begin by engaging children in activities that promote body awareness. This can include activities like yoga, mindfulness exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation. By drawing attention to the sensations in their bodies, children can learn to recognize their internal cues more effectively.
- Create a Sensory Vocabulary
Help children develop a vocabulary to describe their interoceptive experiences. Encourage them to use words like “hungry,” “thirsty,” “tired,” or “anxious” to express their internal states. This can help them communicate their needs more effectively and develop a better understanding of their emotions.
- Emotional Check-ins
Regularly check in with your child about their emotional state. Encourage them to identify and label their emotions, using tools like emotion charts, feelings thermometers or using the program “Zones of
Regulation” that identify your emotional stated by colour s (blue, green, yellow and red). This practice will help them become more aware of their internal emotional states and develop emotional regulation skills.
- Interoceptive Exposure
Expose children to various interoceptive sensations in a controlled and safe environment. This could involve activities like trying different food textures, exposing them to different temperatures, or engaging in exercises that induce changes in heart rate or breathing. This exposure can help children develop a greater tolerance and understanding of their internal sensations.
- Collaborate with Professionals
Consider collaborating with an occupational therapist, who can provide tailored interventions to improve a child’s interoceptive awareness. An occupational therapist will assess the child’s specific needs and develop a comprehensive plan, addressing any underlying issues related to sensory integration.
Conclusion
Fostering interoceptive awareness is essential for children’s overall well-being and development. By focusing on this crucial aspect of sensory integration, we can equip children with the tools they need to navigate their world with greater ease and confidence. To experience the transformative power of interoceptive-focused interventions, do contact us for a consult.